Journal of the American College of Cardiology Recommends Olive Oil
A group of doctors and medical researchers have backed olive oil as a heart-healthy food, while raising concerns about fad diets and the use of coconut and palm oils.
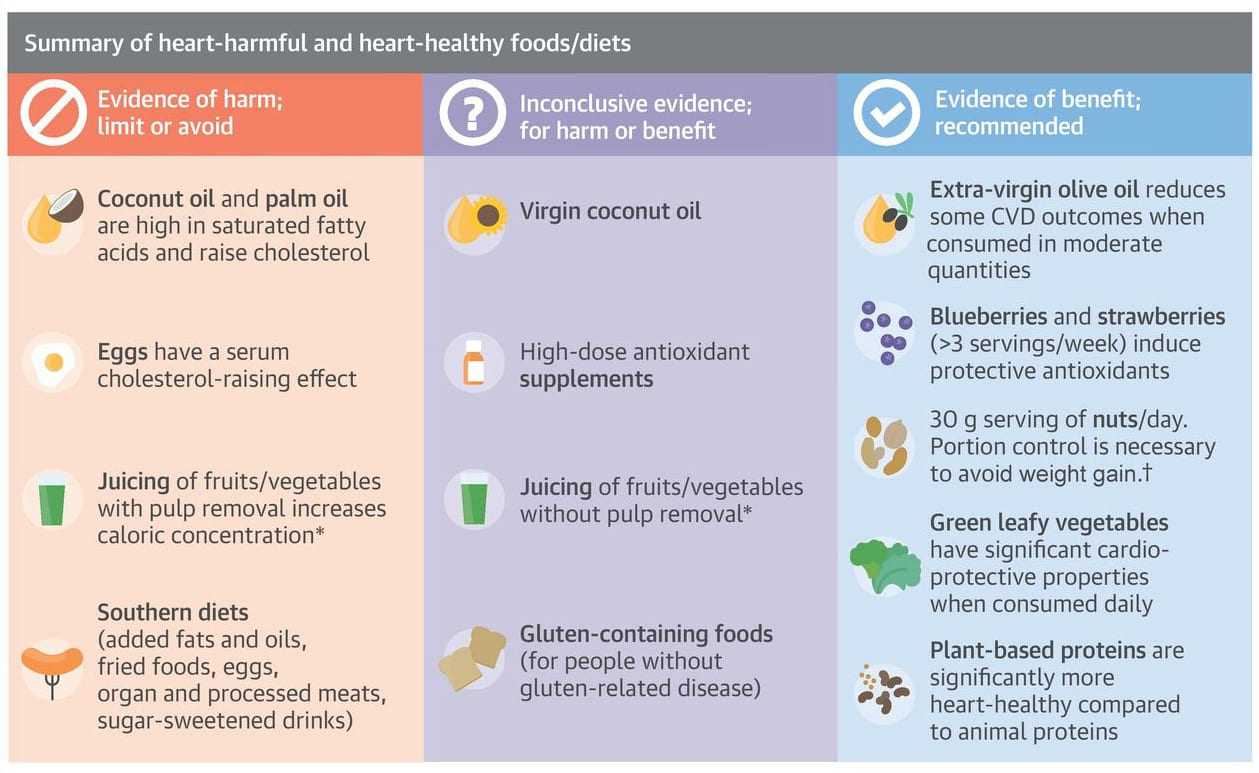
A new analysis published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology supports olive oil as a heart-healthy alternative to butter, while advising against the use of coconut and palm oils. The study also emphasizes the benefits of a largely plant-based diet, with a focus on fruits and leafy green vegetables for promoting heart health.
A new analysis of nutrition studies voices support for olive oil as a heart-healthy substitute for butter, while urging consumers to avoid coconut and palm oils.
A group of doctors and researchers in the U.S. set out to examine the evidence behind a slew of claims, fads, diets and trends related to cardiovascular health. They published their findings in the latest issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The evidence base for olive oil is the most comprehensive, with clear evidence for a benefit in cardiovascular risk reduction.
Chief among the findings is that oils such as olive and canola are healthier than hard fats like butter and margarine. Extra virgin olive oil is singled out in the analysis as being the smartest heart-healthy choice, given the evidence accumulated in a large number of studies conducted on the food.
“The evidence base for olive oil is the most comprehensive, with clear evidence for a benefit in cardiovascular risk reduction,” the scientists said.
At the same time, the researchers suggest that weight-conscious consumers might want to use olive oil only in moderation, given that it is high in calories.
Coconut and palm oils, by contrast, come in for special concern. The analysis says the purported heart-health benefits of such oils are unsubstantiated and recommends that consumers avoid using them.
“There is a great amount of misinformation about nutrition fads,” Andrew Freeman, director of cardiovascular prevention and wellness in the division of cardiology at National Jewish Health in Denver and the paper’s lead author, said in a press release. “However, there are a number of dietary patterns that have clearly been demonstrated to reduce the risk of many chronic diseases, including coronary heart disease.”
The analysis supports eating a largely plant-based diet, noting that evidence suggests the consumption of fruits and leafy green vegetables promote heart health. But researchers warned that patients who use blood thinners should seek a medical consultation to determine what amount of leafy vegetables are best for them. (The high levels of Vitamin K in such vegetables can affect blood clotting.)
The scientists note that a number of health fads such as juicing, gluten-free food and herbal medications have not been shown to offer cardiovascular benefits.
“A generous amount of veggies and fruits, a moderate amount of whole grains and nuts, supplemented with your favorite protein sources of legumes, fish, poultry and lean meats, is a heart-smart, healthy eating plan,” Michael Miller, a professor at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, and a co-author of the review, said in an interview with the Washington Post.
The 52,000-member American College of Cardiology says that The Journal of the American College of Cardiology is the most widely read cardiovascular journal in the world.









