Summer 2022 Was Europe's Hottest on Record

The 2022 global climate report by the European Union Copernicus Climate Change Service revealed record temperatures and extreme weather events, impacting regions across the globe. Human activities are identified as the primary cause of the current global climate crisis, with greenhouse gas emissions continuing to rise, leading to unprecedented levels of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere.
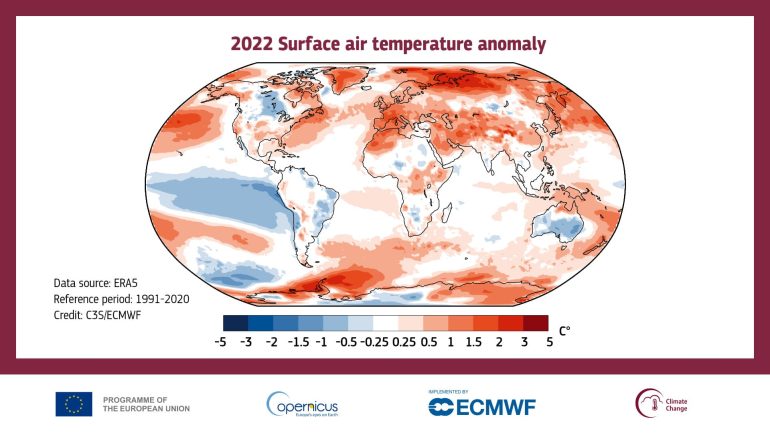
The last eight years have been the warmest ever recorded, and in 2022, the Earth’s surface temperature reached peaks not seen since 1940. Europe also experienced its hottest summer ever.
The 2022 global climate report issued by the European Union Copernicus Climate Change Service shows that 2022 was a record year for extreme weather events. They have plagued farming and affected populations at all latitudes.
Last year, the entire globe was affected by the persistence of the La Nina phenomenon, which provoked an abnormal cooling of the oceans.
Such conditions are typically associated with large-scale weather events, such as the droughts found in vast areas of the U.S., Europe and China or the massive floods that hit Pakistan in August.
Additionally, Pakistan and India were struck by prolonged heatwaves in May and June, with significant heatwaves also hitting China and Europe in subsequent weeks.
See Also:Temperatures Rising Faster in Europe than Anywhere Else, Report FindsThe sweltering summer weighed on the European population and curtailed farming, including olive oil production. Low rainfall levels reported in western and southern Europe contributed to the drought conditions that so heavily slashed agricultural production. The heat waves also did not spare northern Europe.
On top of that, the world’s most relevant olive oil-producing region has seen an increase in the number of wildfires triggered by dry conditions. In 2022, countries such as Spain, France, Germany, and Slovenia recorded the highest wildfire emissions in the last 20 years.
According to Copernicus, surface temperatures in Europe continue to grow more than the global average. In the last 30 years, they have risen twice as fast as any other continent.
“The regions that saw the warmest year on record, including large parts of western Europe, the Middle East, Central Asia and China, South Korea, New Zealand, north-western Africa and the Horn of Africa,” a Copernicus press note highlighted.
In 2022, record temperatures were also reported in the Earth’s polar regions.
Experts consider human activities to be the main trigger of the current global climate crisis. These activities cause the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, thus raising the surface temperature.
More specifically, Copernicus recorded that carbon dioxide concentrations have grown by 2.1 parts per million (ppm), which is consistent with the trend of the past few years. Other relevant polluters, such as methane, have increased by 12 parts per billion (ppb), slightly higher than average but below the record highs of the last two years.
“This resulted in an annual average for 2022 of approximately 417 ppm for carbon dioxide and 1894 ppb for methane. For both gases, this is the highest concentrations from the satellite record, and by including other records, the highest levels for over 2 million years for carbon dioxide and over 800.000 years for methane,” the Copernicus observatory reported.
“Greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide and methane, are the main drivers of climate change, and we can see from our monitoring activities that atmospheric concentrations are continuing to rise with no signs of slowing,” said Vincent-Henri Peuch, director of the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service.









